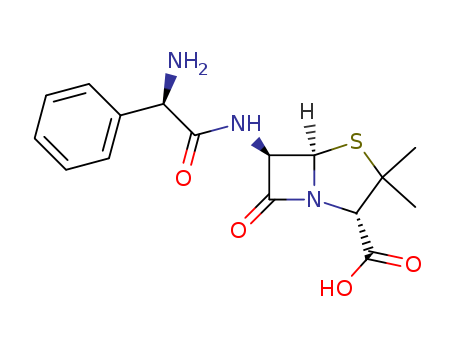
69-53-4
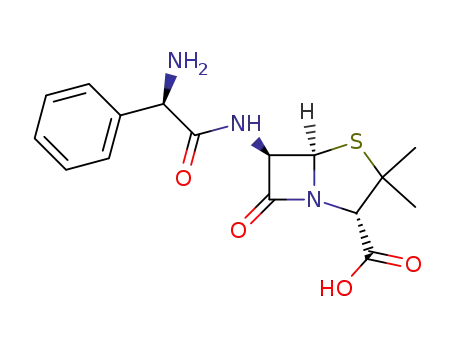
- Product Name:Ampicillin
- Molecular Formula:C16H19N3O4S
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:363.437
Product Details;
CasNo: 69-53-4
Molecular Formula: C16H19N3O4S
Appearance: Crystalline solid
Chinese Factory Supply Wholesale Ampicillin 69-53-4 with Fast Shipping
- Molecular Formula:C16H19N3O4S
- Molecular Weight:363.437
- Appearance/Colour:Crystalline solid
- Melting Point:198-200 °C (dec.)(lit.)
- Refractive Index:1.6320 (estimate)
- Boiling Point:683.9 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:2.5 (COOH)(at 25℃)
- Flash Point:367.4 °C
- PSA:138.03000
- Density:1.45 g/cm3
- LogP:1.34720
- IDLH:85
Ampicillin(Cas 69-53-4) Usage
|
Brand Name(s) |
Human forms include Omnipen, Principen, Totacillin, Polycillin. Injectable forms include Omnipen-N, Polycillin-N, TotacillinN. Veterinary forms include Amp-Equine, and Ampicillin trihydrate (Polyflex). |
|
Description |
Ampicillin is an antibacterial antibiotic from the α-aminobenzyl penicillin group, which differs from penicillin by the presence of an amino group that facilitates penetration through the outer membrane of some gram-negative bacteria. Ampicillin is Semi-synthetic derivative of penicillin that functions as an orally active broad-spectrum antibiotic. Ampicillin acts by interfering directly with the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan, which constitutes the major component of the bacterial cell wall, leading to structural instability and death of bacteria. Ampicillin is a β-lactam antibiotic within the penicillin family. As a member of this family, Ampicillin is susceptible to β-lactamase, which hydrolyzes the β-lactam ring. This broad spectrum antibiotic is effective against gram-positive, gram-negative bacteria and anaerobic bacteria. Ampicillin is widely used in cell culture as a selective agent. As an antibiotic, Ampicillin binds to penicillin binding proteins (PBPs) on a susceptible organism and Inhibits bacterial cell-wall synthesis by inactivating transpeptidases on the inner surface of the bacterial cell membrane. After binding to the PBPs, Ampicilin acts as a structural analogue of acyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine, acylates the transpeptidase enzyme and thereby prevents the cross-linking of the peptidoglycan of the cell wall necessary for the growth of the bacterium. Ampicillin sodium can be used as a selective agent in several types of isolation media. Ampicillin sodium is routinely used to select for cells containing the pcDNA3.1 and pEAK10 resistance plasmids in cell line A904L at an effective concentration of 50 μg/ml. |
|
Chemical Properties |
Crystalline Solid |
|
Originator |
Binotal,Bayer,W. Germany,1962 |
|
Uses |
Ampicillin caused contact dermatitis in a nurse also sensitized to amoxicillin (with tolerance to oral phenoxymethylpenicillin), and in a pharmaceutical factory worker. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A penicillin in which the substituent at position 6 of the penam ring is a 2-amino-2-phenylacetamido group. |
|
Manufacturing Process |
α-Carbobenzyloxyaminophenylacetic acid (0.1 mol), which is obtained by the reaction of equivalent quantities of α-aminophenylacetic acid and benzyl chlorocarbonate in aqueous sodium hydroxide, dissolved in dry acetone is stirred and cooled to approximately -5°C. To this there is added dropwise with continued cooling and stirring a solution of ethyl chlorocarbonate (0.1 mol). After approximately 10 minutes, the acylating mixture is cooled to about -5°C and then is slowly added to a stirred ice-cold mixture of 6-aminopenicillanic acid (0.1 mol), 3% sodium bicarbonate solution (0.1 mol) and acetone. This reaction mixture is allowed to attain room temperature, stirred for an additional thirty minutes at this temperature and then is extracted with ether. The extracted aqueous solution is covered with butanol and the pH adjusted to 2 by the addition of HCl. The acidified aqueous phase is extracted with butanol, the pH of the aqueous phase being adjusted to pH 2 each time. The combined butanol solutions which contain the free acid, α- carbobenzyloxyaminobenzylpenicillin, are washed with water, and are then shaken with water to which sufficient 3% sodium bicarbonate has been added to bring the aqueous phase to pH 7. The process of washing and shaking is repeated with fresh water and bicarbonate solution. The combined aqueous solutions are washed with ether and then are evaporated under reduced pressure and low temperature. The product, the sodium salt of α- carbobenzyloxyaminobenzylpenicillin, is obtained as a yellow solid in a yield of 65%. A suspension of palladium on barium carbonate (3.7 grams of 30%) in water (20 ml) is shaken in an atmosphere of hydrogen at room temperature. The catalyst is then filtered and washed well with water, care being taken that it does not become dry. A solution of the sodium salt of α- carbobenzyloxyaminobenzylpenicillin (4 grams) in water (20 ml) is added to the pretreated catalyst and the suspension is shaken in an atmosphere of hydrogen at room temperature and pressure for one hour. The catalyst is then filtered off, washed well with water, and the combined filtrate and washings adjusted to pH 7 with hydrochloric acid. The resulting solution is evaporated in vacuum at a temperature below 20°C to give α-aminobenzylpenicillin (2.4 grams, 74% yield), which is assayed at approximately 48% pure by the manometric method. |
|
Brand name |
Amcill (Parke-Davis); Omnipen (Wyeth-Ayerst); Polycillin (Apothecon); Principen (Apothecon). |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Antibacterial |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intracerebral route. Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Human systemic effects by ingestion: fever, agranulocytosis, and other blood effects. An experimental teratogen. Mutation data reported. Questionable carcinogen. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NO, and SOx,. |
|
Potential Exposure |
Used as an antibiotic. |
|
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments |
In dogs and cats, ampicillin is not as well absorbed after oral administration as amoxicillin and its oral use has largely been supplanted by amoxicillin. It is used commonly in parenteral dosage forms when an aminopenicillin is indicated in all species. The aminopenicillins, also called the “broad-spectrum” or ampicillin penicillins, have increased activity against many strains of gram-negative aerobes not covered by either the natural penicillins or penicillinase-resistant penicillins, including some strains of E. coli, Klebsiella, and Haemophilus. |
|
Shipping |
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required. |
|
Incompatibilities |
May be incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. |
|
Waste Disposal |
It is inappropriate and possibly dangerous to the environment to dispose of expired or waste pharmaceuticals by flushing them down the toilet or discarding them to the trash. Household quantities of expired or waste pharmaceuticals may be mixed with wet cat litter or coffee grounds, double-bagged in plastic, discard in trash. Larger quantities shall carefully take into consideration applicable DEA, EPA, and FDA regulations. If possible return the pharmaceutical to the manufacturer for proper disposal being careful to properly label and securely package the material. Alternatively, the waste pharmaceutical shall be labeled, securely packaged and transported by a state licensed medical waste contractor to dispose by burial in a licensed hazardous or toxic waste landfill or incinerator. |
|
Who Evaluation |
Evaluation year: 2017 |
InChI:InChI=1/C16H19N3O4S/c1-16(2)11(15(22)23)19-13(21)10(14(19)24-16)18-12(20)9(17)8-6-4-3-5-7-8/h3-7,9-11,14H,17H2,1-2H3,(H,18,20)(H,22,23)/t9-,10-,11+,14-/m1/s1
69-53-4 Relevant articles
Penicillin Acylase Catalysed Synthesis of Ampicillin in Hydrophilic Organic Solvents
Van Langen, Luuk M.,Oosthoek, Natasja H. P.,Van Rantwijk, Fred,Sheldon, Roger A.
, p. 797 - 801 (2003)
Penicillin acylase (EC 3.5.1.11) from Al...
Penicillin Acylase-Catalyzed Solid-State Ampicillin Synthesis
Youshko,Svedas
, p. 894 - 898 (2002)
The ability of immobilized penicillin ac...
Stability of aqueous bacampicillin suspension
Fujiwara,Kawashima,Yamada,Nakai
, p. 345 - 353 (1988)
-
Efficient enzymatic synthesis of ampicillin using mutant Penicillin G acylase with bio-based solvent glycerol
Deng, Senwen,Ma, Xiaoqiang,Sun, Ming,Wei, Dongzhi,Su, Erzheng
, p. 31 - 34 (2016)
To fulfill the industry demand of ampici...
An efficient synthesis of ampicillin on magnetically separable immobilized penicillin G acylase
Xue, Ping,Song, Xiao Dan,Cao, Xue Rong
, p. 765 - 768 (2010)
Penicillin G acylase (PGA) was immobiliz...
A high-throughput pH-based colorimetric assay: application focus on alpha/beta hydrolases
Paye, Mariétou F.,Rose, Harrison B.,Robbins, John M.,Yunda, Diana A.,Cho, Seonggeon,Bommarius, Andreas S.
, p. 80 - 90 (2018/03/24)
Research involving α/β hydrolases, inclu...
IMMORTALIZED STEM CELL, COMPOSITIONS, PREPARATIONS AND USES THEREOF
-
, (2018/01/14)
The purpose of the present invention is ...
Amino ester hydrolase from Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris, ATCC 33913 for enzymatic synthesis of ampicillin
Blum, Janna K.,Bommarius, Andreas S.
scheme or table, p. 21 - 28 (2010/12/19)
α-Amino ester hydrolases (AEH) are a sma...
69-53-4 Process route
-
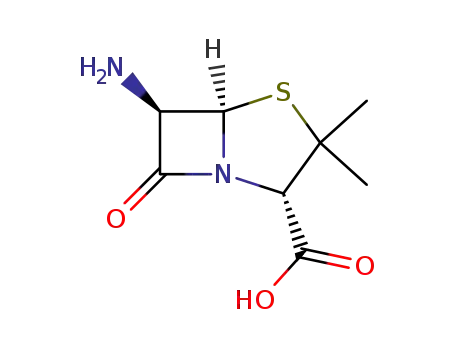
- 551-16-6
6-Aminopenicillanic Acid
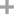
-
- 24461-61-8
(R)-Phenylglycine methyl ester

-
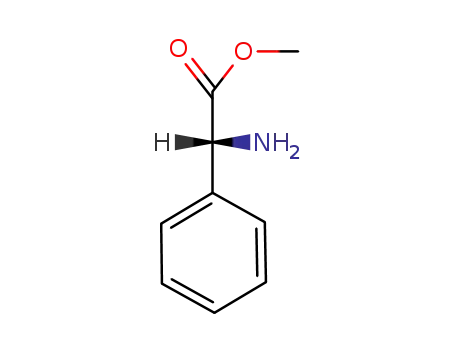
- 69-53-4
ampicillin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With phosphate buffer; Eupergit C-immobilized penicillin acylase (30 U/mg); sodium sulfate; at 20 ℃; pH=6.5; Further Variations:; Reagents; water content; Product distribution; Kinetics; solid phase reaction;
|
70% |
|
at 30 ℃; for 3h; Yield given; Pseudomonas melanogenum KY 3987 and KY 8540;
|
|
|
With penicillin acylasefrom Escherichia coli; water;
|
|
|
With βF24G mutant of penicillin G acylase from Alcaligenes faecalis, immobilized onto an epoxy carrier LH-EP; In glycerol; at 20 ℃; pH=5.8; Concentration; pH-value; Temperature; Green chemistry; Enzymatic reaction;
|
-

- 551-16-6
6-Aminopenicillanic Acid

-

- 69-53-4
ampicillin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With (S)-Phenylglycine methyl ester; In ethylene glycol; at 20 ℃; for 48h; Enzymatic reaction;
|
96.7% |
69-53-4 Upstream products
-
3511-16-8
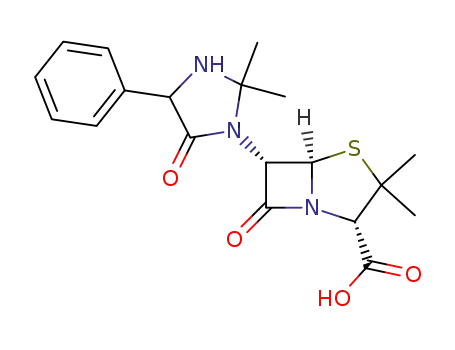
6-epi-hetacillin
-
40439-01-8
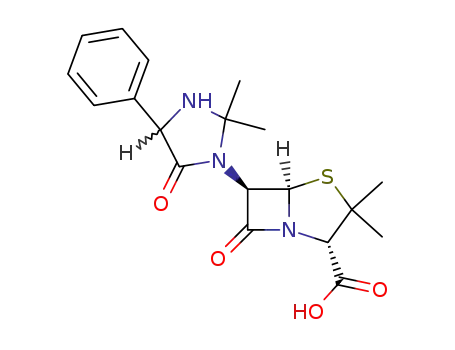
hetacillin
-
551-16-6

6-Aminopenicillanic Acid
-
60686-78-4
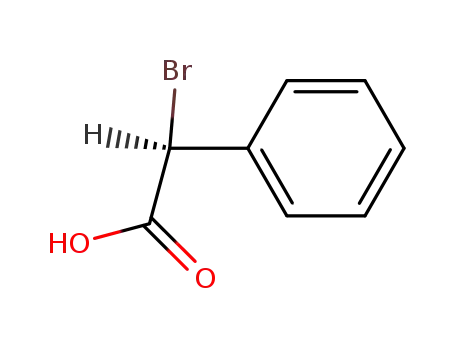
(+)-(S)-α-bromophenylacetic acid
69-53-4 Downstream products
-
94595-14-9
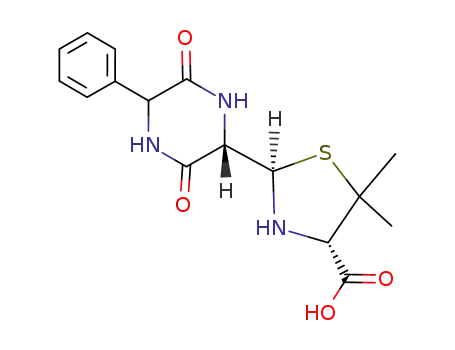
2-(3,6-dioxo-5-phenylpiperazine-2-yl)-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid
-
65029-03-0
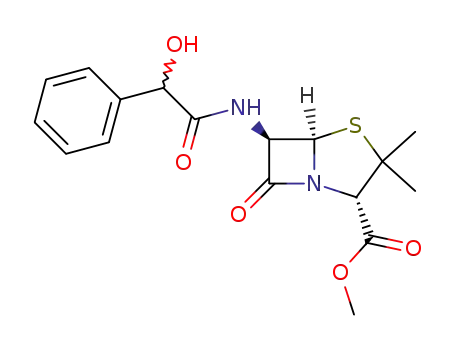
6β-((Ξ)-2-hydroxy-2-phenyl-acetylamino)-penicillanic acid methyl ester
-
14085-40-6
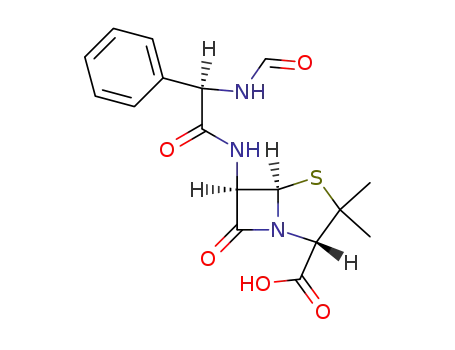
6β-((R)-2-formylamino-2-phenyl-acetylamino)-penicillanic acid
-
57421-55-3
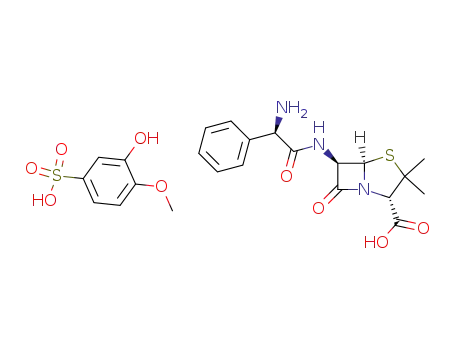
6β-((R)-2-amino-2-phenyl-acetylamino)-penicillanic acid; 3(or 4)-hydroxy-4(or 3)-methoxy-benzenesulfonate
Relevant Products
-
Corticotropin
CAS:9002-60-2
-
V-9-M cholecystokinin nonapeptide
CAS:99291-20-0
-
N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-p-phenylenediamine sulphate
CAS:54381-16-7