78-44-4
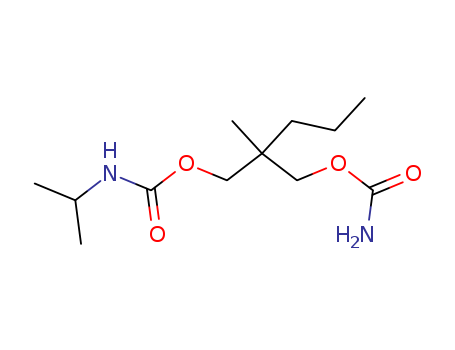
- Product Name:Carisoprodol
- Molecular Formula:C12H24N2O4
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:260.334
Product Details;
CasNo: 78-44-4
Molecular Formula: C12H24N2O4
Appearance: White powder.
Quality Factory Supply Top Purity Carisoprodol 78-44-4 On Stock
- Molecular Formula:C12H24N2O4
- Molecular Weight:260.334
- Appearance/Colour:White powder.
- Melting Point:92-92 oC
- Refractive Index:1.4560 (estimate)
- Boiling Point:423.412 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:pKa 4.2 (Uncertain)
- Flash Point:209.872 °C
- PSA:90.65000
- Density:1.056 g/cm3
- LogP:3.11390
Carisoprodol(Cas 78-44-4) Usage
|
Description |
Carisoprodol (Item No. 30778) is an analytical reference standard categorized as a skeletal muscle relaxant. It also has sedative properties. Carisoprodol is regulated as a Schedule IV compound in the United States. This product is intended for research and forensic applications. |
|
Chemical Properties |
White Solid |
|
Originator |
Soma,Wallace,US,1959 |
|
Uses |
Carisoprodol suppresses interneuronal action of reticular formation of the spinal cord. It is used as an adjuvant drug for loss of flexibility of skeletal muscle as well as for relieving pain caused therein. Synonyms of this drug are rela, soma, carisoma, and sanoma. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A carbamate ester that is the mono-N-isopropyl derivative of meprobamate (which is a significant metabolite). Carisoprodol interrupts neuronal communication within the reticular formation and spinal cord, resulting in sedation and alter tion in pain perception. It is used as a muscle relaxant in the symptomatic treatment of musculoskeletal conditions associated with painful muscle spasm. |
|
Preparation |
Carisoprodol is Prepared by reaction of 2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-pro-panediol with phosgene and ammonium hydroxide, then with isopropyl isocyanate. |
|
Manufacturing Process |
A cooled 10% solution of 1 mol of phosgene in toluene was added with stirring to a cooled solution of 1 mol of 2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol and 2 mols of dimethylaniline also dissolved in toluene, at such a rate that the temperature of the mixture was maintained at about 25°C. The mixture was allowed to remain at this temperature for several hours, then cooled and extracted with cold 5% hydrochloric acid solution to remove the dimethylaniline. The toluene layer was dried using a suitable drying agent and the 2-methyl-2-propyl-3-hydroxypropyl chlorocarbonate used in subsequent reactions in the form of its solution in anhydrous toluene.A quantity of solution obtained as described containing 0.1 mol of the chlorocarbonate was treated with 0.2 mol of anhydrous isopropylamine and allowed to react at ordinary room temperature. The solution was cooled, extracted with dilute hydrochloric acid and the organic layer concentrated by evaporation of the solvent. The crude monocarbamate was purified by distilling at 86° to 88°C at about 0.01 mm. It was a clear, viscous liquid.21.7 g (0.1 mol) of N-isopropyl-2-methyl-2-propyl-3-hydroxypropylcarbamate and 7.5 g (0.11 mol) of anhydrous sodium cyanate are stirred in 200 ml anhydrous chloroform in a suitable vessel equipped with a gas inlet tube,stirrer and thermometer. While cooling the vessel, anhydrous hydrogen chloride is passed into the stirred mixture slowly for 5 hours maintaining the temperature between 0° and 5°C. Alternatively ethyl urethane in the presence of aluminum isopropylate as a catalyst may be used in place of the sodium cyanates and HCl. The mixture is then allowed to stand at room temperature overnight.The solid material is separated by filtration and the chloroform solution concentrated to an oil under reduced pressure. The oil is dissolved in 50 ml of trichloroethylene, the solution treated with charcoal, filtered and the filtrate added to 125 ml of hexane. The crystalline material which forms on standing at refrigerator temperature is removed by filtration, washed with light petroleum ether and dried at about 50°C. Approximately 20 g of product are obtained. On recrystallizing from trichloroethylene-hexane, 17.8 g of purified compound are obtained, MP 89° to 91°C. |
|
Brand name |
Rela (Schering); Soma (Medpointe). |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Muscle relaxant |
|
General Description |
Carisoprodol, N-isopropyl-2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol dicarbamate, 2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol carbamate isopropylcarbamate(Soma), is the mono-N-isopropyl–substituted relative ofmeprobamate. The structure is given in the discussion ofmeprobamate. It is indicated in acute skeletomuscular conditionscharacterized by pain, stiffness, and spasm. As canbe expected, a major side effect of the drug is drowsiness. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Carisoprodol is a carbamate ester. Carbamates are chemically similar to, but more reactive than amides. Like amides they form polymers such as polyurethane resins. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is produced by the combination of active metals or nitrides with carbamates. Strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides are incompatible with carbamates. |
|
Health Hazard |
SYMPTOMS: The most common symptoms of exposure to Carisoprodol are drowsiness and hives. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, vertigo, ataxia, tremors, agitation, irritability, headache, insomnia, fainting, hiccups, visual disturbances, asthma, fever, hypotension, excitement and paralysis. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Flash point data for Carisoprodol are not available, but Carisoprodol it probably combustible. |
|
Synthesis |
Carisoprodol, N-iso-propyl-2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-propanediol (15.3.12), is synthesized by reacting 2-methyl-2-propylpropanediol-1,3 dicarbamate with 1 mol of phosgene, forming the chloroformate (15.3.10), from which carbamate (15.3.11) is formed by reacting it with isopropylamine. Reacting this with either urethane or sodium cyanate gives carisoprodol (15.3.12). |
InChI:InChI=1/C12H24N2O4/c1-5-6-12(4,7-17-10(13)15)8-18-11(16)14-9(2)3/h9H,5-8H2,1-4H3,(H2,13,15)(H,14,16)
78-44-4 Relevant articles
Catalytic One-Pot Oxetane to Carbamate Conversions: Formal Synthesis of Drug Relevant Molecules
Guo, Wusheng,Laserna, Victor,Rintjema, Jeroen,Kleij, Arjan W.
supporting information, p. 1602 - 1607 (2016/10/13)
Oxetanes are versatile building blocks i...
CARBAMATE REDUCERS OF SKELETAL MUSCLE TENSION
-
Page/Page column 11, (2010/04/23)
The present invention relates to new car...
PREPARATION OF CARBAMATES
Gorodetskii, L. Sh.,Volzhina, O. N.,Kuznetsova, I. A.,Alekseeva, E. N.
, p. 474 - 477 (2007/10/02)
-
78-44-4 Process route
-
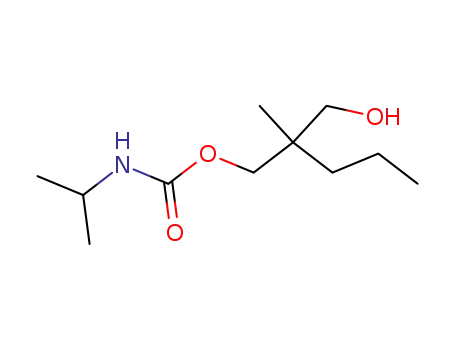
- 25462-17-3
N-Mono-isopropyl-2-methyl-2-n-propylpropane-1,3-diol carbamate
-
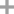
- 917-61-3
sodium isocyanate

-
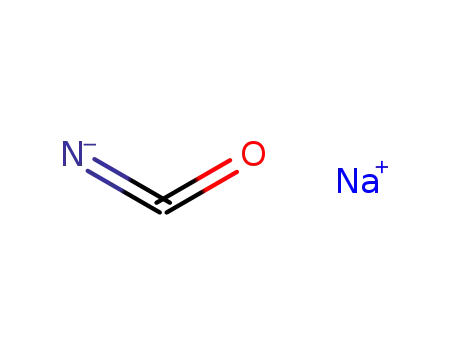
- 78-44-4,8053-63-2
carisoprodol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogenchloride; In dichloromethane; at -2 - 2 ℃; for 10h;
|
80% |
|
N-Mono-isopropyl-2-methyl-2-n-propylpropane-1,3-diol carbamate; sodium isocyanate; With hydrogenchloride; In dichloromethane; at 0 ℃; for 2.5h;
With sodium hydrogencarbonate; In dichloromethane; pH=8;
|
-

- 25462-17-3
N-Mono-isopropyl-2-methyl-2-n-propylpropane-1,3-diol carbamate

-
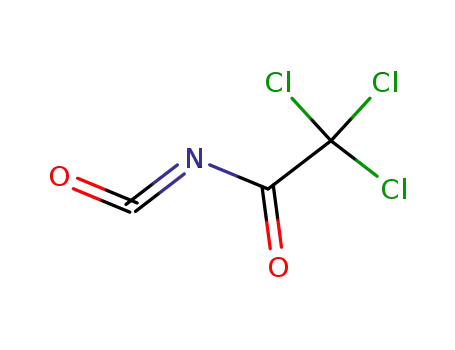
- 3019-71-4
Trichloroacetyl isocyanate

-

- 78-44-4,8053-63-2
carisoprodol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
N-Mono-isopropyl-2-methyl-2-n-propylpropane-1,3-diol carbamate; Trichloroacetyl isocyanate; In methanol; dichloromethane; at 0 - 25 ℃; for 4h;
With potassium carbonate; In methanol; dichloromethane; at 25 ℃; for 4h;
|
96% |
78-44-4 Upstream products
-
75-44-5
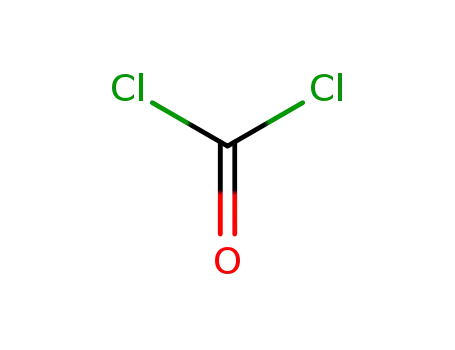
phosgene
-
25462-17-3

N-Mono-isopropyl-2-methyl-2-n-propylpropane-1,3-diol carbamate
-
917-61-3

sodium isocyanate
-
7148-50-7
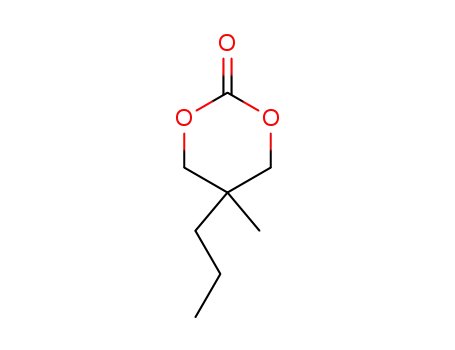
5-Methyl-5-n-propyl-1,3-dioxan-2-one
78-44-4 Downstream products
-
25648-91-3
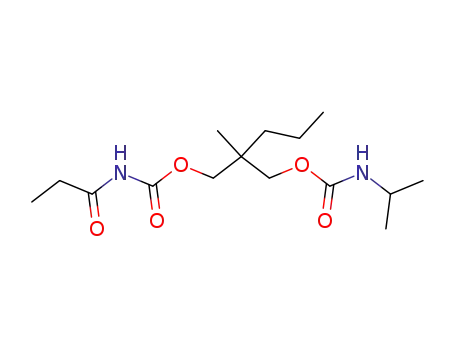
N-Isopropyl-N'-propionyl-2-methyl-2-propyl-1,3-dicarbamoyloxy-propan
Relevant Products
-
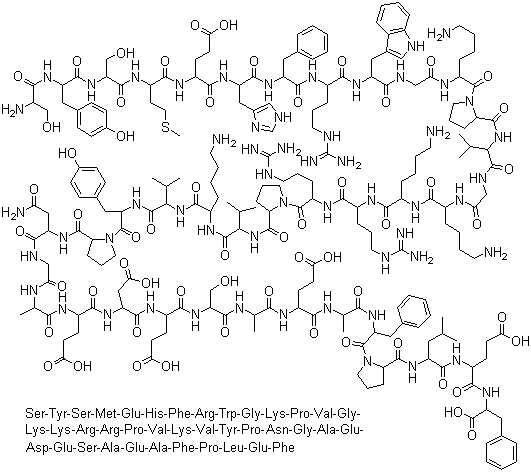
Corticotropin
CAS:9002-60-2
-
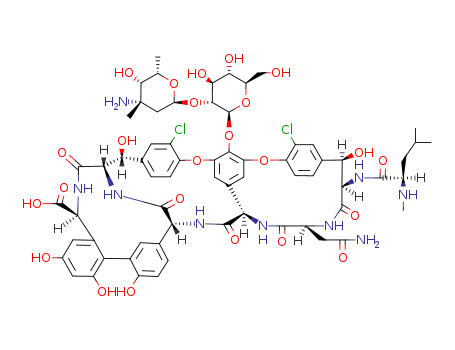
Vancomycin
CAS:1404-90-6
-
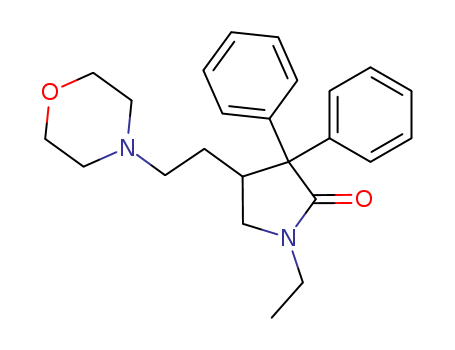
Doxapram
CAS:309-29-5